Track: Fungal Skin Infections
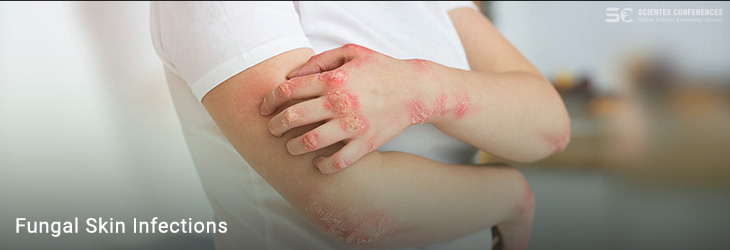
Fungal skin infections, caused by dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds, present a significant challenge in dermatology due to their varied manifestations and recurrence rates. These infections often affect specific areas of the skin, leading to distinct clinical patterns that require accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment. Advances in antifungal therapies and diagnostic techniques have improved the management of these conditions. This overview will explore the common fungal infections, emphasizing their symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and treatment methodologies.
Tinea Corporis (Ringworm):
Tinea Corporis, commonly known as ringworm, is a fungal infection characterized by round, scaly patches on the skin with a raised, red border. It typically spreads through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated objects. Treatment often involves topical antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or terbinafine, with oral antifungals considered for severe or widespread cases.
Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot):
Tinea Pedis, or athlete's foot, affects the feet, causing itching, burning, and scaling between the toes or on the soles. It is highly contagious and commonly spread in damp environments like locker rooms and swimming pools. Effective management includes topical antifungal powders or creams, and keeping the feet dry to prevent recurrence.
Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch):
Tinea Cruris, known as jock itch, primarily affects the groin area, presenting as a red, itchy rash with well-defined edges. It can be aggravated by moisture and friction, making it common among athletes and individuals with sweaty or tight clothing. Treatment typically involves topical antifungal agents, maintaining good hygiene, and avoiding tight clothing.
Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor):
Tinea Versicolor, or pityriasis versicolor, causes discolored patches on the skin that can be lighter or darker than the surrounding areas. This infection is due to an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, commonly found on the skin. Treatment options include topical antifungal lotions or shampoos, and oral antifungals for more severe cases.
Candida Dermatitis:
Candida Dermatitis is a fungal infection caused by Candida yeast, often affecting moist areas like skin folds. It presents as red, inflamed skin with possible pustules or scaling. Antifungal creams or ointments, along with measures to reduce moisture and friction, are the primary treatments. In persistent cases, oral antifungals may be necessary.
Scientific Highlights
- Skin Diseases: Acne, Psoriasis, Dermatitis
- Cosmetic Surgery
- Dermatopathology
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Aesthetic Medicine
- Plastic Surgery
- Diet & Nutritional Supplements for Healthy Skin
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Dermato oncology
- Dermatology
- Trichology and Hair Transplantation
- Vitiligo Treatment
- Rhinoplasty and Otoplasty
- Fungal Skin Infections
- Cosmetology
- Skincare Treatment
- Dermatologic Disorders
- Clinical Trial and Case Reports
- Teledermatology & AI Diagnostics
- Wound Care
- Leprosy in Modern Dermatology
- Onychomycosis
- Regenerative Aesthetics
- Targeted Drug Delivery Systems
- GI Health & Skin


