Track: Regenerative Aesthetics
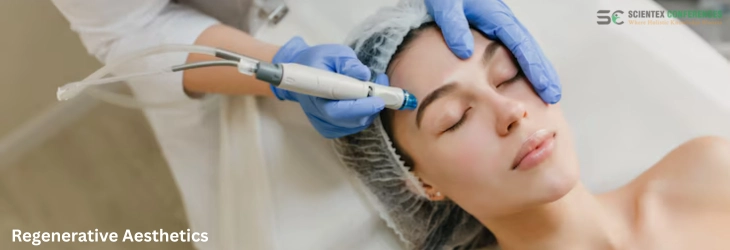
The field of Regenerative Aesthetics represents a groundbreaking shift from traditional cosmetic enhancement toward biologically driven rejuvenation. This session delves into therapies that activate the body’s own regenerative potential - promoting skin health, tissue repair, and long-lasting aesthetic outcomes. With science-backed approaches such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP), stem cell-based therapies, exosomes, biostimulators, and collagen inducers, regenerative aesthetics is not only reshaping anti-aging protocols but also redefining the future of dermatologic and cosmetic interventions. Participants will gain a deep understanding of how to integrate regenerative tools into clinical practice, personalize treatments, and ensure both safety and efficacy.
The Science of Regeneration in Aesthetic Medicine:
The science of regeneration in aesthetic medicine is rooted in the principles of regenerative biology, particularly as it applies to combating skin aging. Central to this field are processes such as cellular senescence and oxidative stress, both of which contribute to the degradation of skin structure and function over time. Emerging therapies aim to reverse or mitigate these effects by targeting cellular pathways that restore vitality and promote tissue renewal. Understanding and monitoring key biomarkers of skin regeneration such as collagen synthesis, elastin production, and specific growth factors are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of anti-aging treatments and developing personalized aesthetic interventions.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) & Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF):
Regenerative treatments such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and growth factor therapies work by stimulating cellular repair and collagen production through the release of bioactive proteins and cytokines. The mechanism of action involves activating tissue regeneration pathways that enhance skin texture, tone, and elasticity. Proper preparation protocols—including centrifugation parameters, anticoagulant use, and activation methods are critical for ensuring efficacy and consistency. Clinically, these therapies are widely applied in facial rejuvenation, treatment of acne scars, hair regrowth, and under-eye revitalization, offering minimally invasive solutions with natural-looking results. When combined with microneedling, laser treatments, or dermal fillers, regenerative therapies can amplify outcomes by synergistically enhancing collagen remodeling and skin renewal.
Stem Cells & Exosome Therapy:
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) have emerged as powerful tools in regenerative aesthetics due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types and secrete growth factors that promote tissue repair and rejuvenation. A key component of their therapeutic effect lies in exosomes-extracellular vesicles that facilitate intercellular communication and play a pivotal role in stimulating collagen synthesis, reducing inflammation, and enhancing overall skin regeneration. As interest in these biologics grows, so do regulatory and ethical considerations, particularly concerning sourcing, standardization, and long-term safety. Ensuring compliance with evolving guidelines and addressing ethical questions around stem cell use are essential for the responsible advancement of these promising therapies in clinical practice.
Biostimulators & Injectable Collagen Inducers:
Biostimulatory injectables such as Sculptra (poly-L-lactic acid, PLLA), Radiesse (calcium hydroxylapatite, CaHA), and polynucleotides have gained popularity in dermatology for their ability to stimulate collagen production and improve skin quality over time. These products work through distinct mechanisms PLLA induces fibroblast activation, CaHA provides immediate volume with gradual biostimulation, and polynucleotides promote cellular repair and hydration. Treatment protocols vary depending on the agent, with careful attention to dilution, injection technique, and session intervals to optimize results and minimize adverse effects. Safety profiles are generally favorable when administered by trained professionals, though patient selection is critical to achieving desired long-term outcomes. Ideal candidates are those seeking gradual, natural-looking rejuvenation with a focus on skin texture, elasticity, and contour refinement.
Combination Approaches in Regenerative Aesthetics:
Layering regenerative techniques with energy-based devices such as radiofrequency (RF) and lasers has become a cornerstone of advanced aesthetic dermatology, offering synergistic benefits in collagen remodeling, skin tightening, and overall rejuvenation. This integrated approach enhances treatment efficacy by combining the biological stimulation of regenerative therapies with the controlled tissue remodeling induced by energy-based technologies. Creating personalized treatment maps based on individual factors like skin type, age, and aesthetic goals is essential for optimizing outcomes and minimizing risks. Case presentations with before-and-after evidence further support the effectiveness of these combination protocols, showcasing significant improvements in texture, tone, and facial contours while reinforcing the value of customized, multimodal treatment plans.
Beyond the Skin: Psychosocial Benefits of Regenerative Aesthetics:
Regenerative therapies play a transformative role in trauma recovery, post-surgical healing, and burn rehabilitation by accelerating tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and minimizing scarring. Treatments utilizing growth factors, stem cells, and exosomes support cellular regeneration and improve skin integrity in damaged areas, offering significant functional and aesthetic benefits. Beyond physical healing, these therapies also contribute to emotional well-being by enhancing self-perception and confidence. Biologic restoration not only restores the skin’s appearance but also empowers individuals to regain a sense of normalcy and self-esteem, making regenerative medicine a powerful tool in both medical and psychological recovery.
Scientific Highlights
- Skin Diseases: Acne, Psoriasis, Dermatitis
- Cosmetic Surgery
- Dermatopathology
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Aesthetic Medicine
- Plastic Surgery
- Diet & Nutritional Supplements for Healthy Skin
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Dermato oncology
- Dermatology
- Trichology and Hair Transplantation
- Vitiligo Treatment
- Rhinoplasty and Otoplasty
- Fungal Skin Infections
- Cosmetology
- Skincare Treatment
- Dermatologic Disorders
- Clinical Trial and Case Reports
- Teledermatology & AI Diagnostics
- Wound Care
- Leprosy in Modern Dermatology
- Onychomycosis
- Regenerative Aesthetics
- Targeted Drug Delivery Systems
- GI Health & Skin


